Phishing 101, How to detect a Deceptive URL
Introduction
Believe it or not but lately people have been setting up a lot of websites that look like the real thing but secretly instal virus', steal usernames and passwords and in some cases bank details.
Subdomain / Domain Confusion
One of the most important things to know about this phenomenon is how a URL works;
A URL consists of three or two components
The last section is the Top Level Domain (TLD) such as .com, .net, .org or .com.au or .co.uk
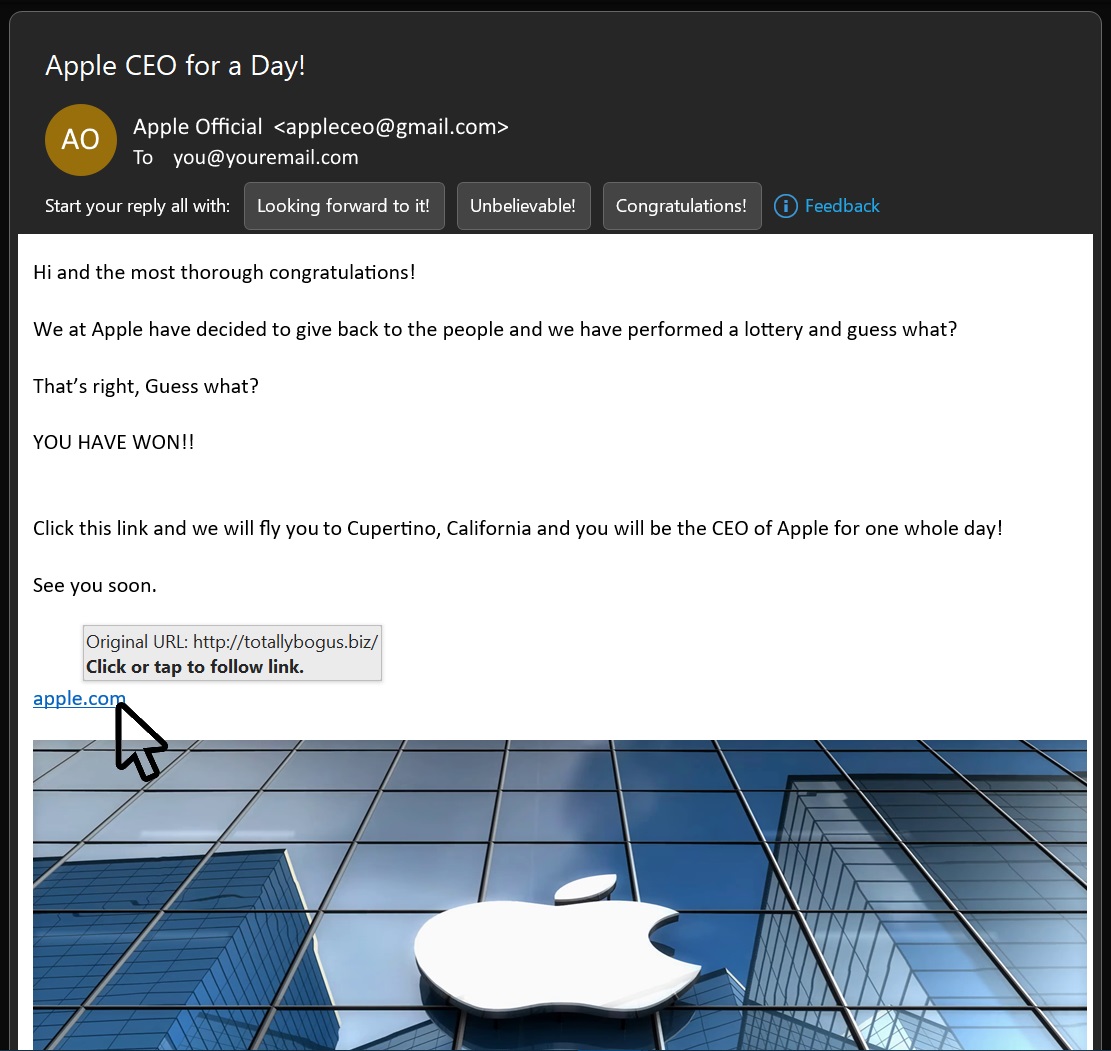
The section left of that is the Domain, this is the section that a company registers such as in our case, pcuser, which we rent from an Domain Name Registrar, or the Apple in apple.com (tip: its not case-sensitive, nor are emails).
Optionally, there may be what’s known as a Subdomain that separated by a dot represents in actuality a whole new website such as the Shop in shop.apple.com which is controlled by the owner of the apple.com domain. The moral of the story is that the owner of the domain can name the subdomain to whatever they like as only the domain has to be registered, for instance the owner of the domain abcde.com could create a subdomain called officialiphonestore.abcde.com.
So knowing that, out of two URL's shop.apple.com or apple.server2.com which one is genuine?
One belongs to Apple.com which is owned by Apple.com (which is Apple) and the other is in control of whomever has registered the domain server2.com
Therefore if you receive an email and it looks genuine and it says that there's a great software-based hardware upgrade for your Phone and all it takes is to visit apple.server2.com and pay a fee, then its probably bogus.
Is google.com the same as google.net?
No, absolutely not.
Infact google.net is probably a site to be avoided for such reasons.
Domains registered upon different Top Level Domains (.net, .com, .net.au) are wholly different entities and registered separately.
Although that said it is fairly common for companies to register their domain upon multiple Top Level Domains on a regional basis. For example amazon.com.au and amazon.com though (unless set up to point to the same website) are actually totally different sites (but probably look the same) or something along those lines.
Potential Effects
The effects of falling for this and clicking on a malicious website can be really severe.
Simply visiting the site can install a virus on your computer, as simple as that, called a Drive-By Download.
Entering your Apple credentials (to supposedly log in) or any personal details (to supposedly verify its you) on an immitation site like this will mean these details are now in the possession of the Phisher and he/she can now login to the genuine Apple site (on your behalf) and do anything you could do (that's why some companies send a verification SMS) and to boot, knows some of your private details for later use.
Finally, if you enter your credit card details then ofcourse the Phisher now has that too and can (and very likely will, and quickly) go on a shopping spree at your expense.
Also, recently people have been taking this one step further and once their in changing the login credentials and password. This (and another attack called Cookie Stealing, which is simply taking the authentication cookie) is the reason why people can be wholly locked out of their account and also one of the main reasons why Two Factor Authentication exists.
If unsure about a link
If unsure about a web address and it looks innocuous then a good way to verify if an address is valid is to "google it" (google.com) first. For instance if you "google" Amazon then the real address or addresses should be first or high on the list and contain an appropriate description. Also you can directly search for a Company and a location such as searching for "Amazon Australia" which should produce amazon.com.au.
Also, these attacks are absolutely growing in sophistication and prevalence and it is also possible that emails including links like these can come from (but not necesariy written by) people you that you are in email contact with on a frequent or close basis.
Therefore, if someone sends you a questionable link then it may be worth double checking with the sender via an alternate method ie in person or on the telephone and this approach is slowly becoming common practice.
Though, for some reason or another these attacks are slowly becoming more and more part of peoples reality and while this guide will definitely stop the vast bulk of Phishing Attacks, in reality no-one is immune.
Obfuscation, Is the blue link in a email really the address?
Do you remember when sometimes links used to say "Click Here" instead of a url like apple.com/shop/iphone13?
Well, nothings changed and the displayed text is still separate (or can be) from the url link.
The solution to this is to hover the mouse cursor over the link text and inspect it to see if the link is genuine and what it claims to be and the same rules mentioned in the first section of this page completely apply.